How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of drone operation, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced techniques and legal considerations. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your skills, this resource will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
We’ll explore the essential steps involved in each stage of drone flight, from understanding your drone’s controls and navigating different flight modes to mastering advanced maneuvers and troubleshooting common issues. We’ll also delve into the crucial aspects of safety, legal regulations, and ethical considerations to ensure your drone operations are both successful and responsible.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures: How To Operate A Drone
A thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for safe and responsible drone operation. It minimizes risks and ensures optimal performance. This section details the steps involved in a comprehensive pre-flight inspection, relevant safety regulations, and common troubleshooting.
Pre-Flight Inspection Steps
Before each flight, a comprehensive inspection is necessary. This includes verifying battery levels, inspecting propellers for damage, and confirming GPS signal acquisition. A systematic approach ensures nothing is overlooked.
- Battery Check: Ensure the drone battery is fully charged and in good condition. Check for any signs of damage or swelling.
- Propeller Check: Inspect each propeller for cracks, chips, or any signs of damage. Replace damaged propellers immediately.
- GPS Signal Acquisition: Allow sufficient time for the drone to acquire a strong GPS signal before takeoff. This ensures accurate positioning and flight stability.
- Gimbal Check (if applicable): Verify that the gimbal is functioning correctly and is securely mounted.
- Visual Inspection: Conduct a visual inspection of the entire drone, checking for any loose parts or damage.
Drone Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Adhering to safety regulations and best practices is paramount. This ensures the safety of yourself, others, and property.
- Always check local drone regulations and airspace restrictions before flying.
- Maintain visual line of sight with your drone at all times.
- Avoid flying near airports, hospitals, or other sensitive areas.
- Never fly your drone over crowds of people.
- Be aware of the weather conditions before and during flight.
- Fly responsibly and respectfully, considering the privacy of others.
Pre-Flight Procedure Flowchart
A visual representation of the pre-flight procedure can be helpful. The flowchart would begin with “Power On,” followed by “Battery Check,” “Propeller Check,” “GPS Signal Acquisition,” and finally “Visual Inspection,” leading to “Ready for Takeoff” or “Troubleshooting” if issues are detected.
Common Pre-Flight Issues and Solutions
Several common issues can arise during pre-flight checks. This table Artikels some potential problems and their solutions.
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Low Battery | Charge the battery fully. |
| Damaged Propeller | Replace the damaged propeller. |
| Weak GPS Signal | Move to an area with better GPS reception. |
| Gimbal Malfunction | Check gimbal connections and calibrate if necessary. |
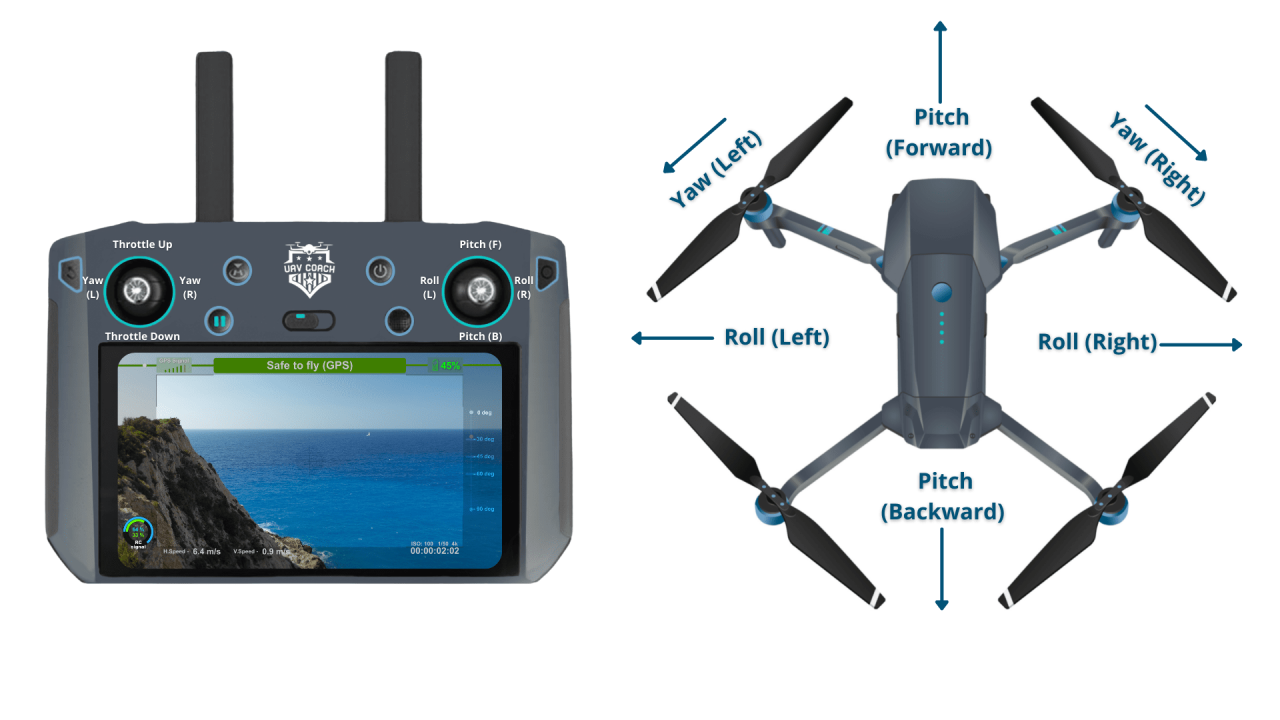
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding drone controls and navigation is essential for safe and efficient operation. This section covers the basic controls, flight modes, and the importance of GPS signal.
Basic Drone Controls
Most drones utilize two control sticks. The left stick typically controls the drone’s altitude and yaw (rotation), while the right stick controls the drone’s forward/backward and left/right movement. Buttons on the controller provide additional functionalities like taking photos, recording videos, and returning to home.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of autonomy and control. Altitude hold maintains a consistent altitude, GPS mode uses GPS for precise positioning, and attitude mode allows for more agile maneuvers.
- Altitude Hold: Maintains a constant altitude, simplifying flight control.
- GPS Mode: Utilizes GPS for precise positioning and stability.
- Attitude Mode: Provides more responsive and agile control, ideal for experienced pilots.
Smooth Drone Maneuvers
Smooth and controlled maneuvers are achieved through gentle and precise stick movements. Avoid abrupt changes in direction or speed to prevent jerky movements and potential crashes.
GPS Signal and Drone Navigation
The GPS signal is crucial for drone navigation, providing precise location data. A strong GPS signal is essential for features like GPS mode, return-to-home (RTH), and waypoint navigation.
Drone Control Interfaces, How to operate a drone
Different drones may offer varying control interfaces, including dedicated controllers, smartphone apps, and even VR headsets. Each interface offers a unique user experience and level of control.
Taking Off, Landing, and Basic Maneuvers
Safe takeoff, landing, and basic maneuvers are fundamental skills for every drone pilot. This section details the steps involved in these crucial flight phases.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone which covers pre-flight checks and maneuvering techniques. Mastering these skills ensures safe and efficient drone operation, ultimately leading to a positive flying experience.
Safe Drone Takeoff
A safe takeoff involves a step-by-step procedure ensuring stability and control. Begin with a pre-flight check, followed by powering on the drone and controller. Once a strong GPS signal is acquired, gently lift the drone into the air using the control sticks. Maintain a steady ascent, avoiding abrupt movements.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and enjoyable drone operation.
Safe Drone Landing
A controlled landing involves a gradual descent to the ground. Begin by slowing the drone’s movement, then initiate a gentle descent using the control sticks. Maintain a stable descent until the drone touches down softly on the ground. Power off the drone and controller once it is safely landed.
Basic Drone Maneuvers
Basic maneuvers such as hovering, ascending, descending, and turning are essential for controlled flight. Practice these maneuvers in a safe and open area before attempting more complex flight patterns.
Simple Flight Pattern Sequence
A simple flight pattern might involve taking off, hovering for a few seconds, ascending to a specific altitude, moving forward, turning, descending, and then landing. This sequence helps practice basic control and coordination.
Correct Posture and Hand Movements
The optimal posture involves sitting or standing comfortably with good support. The hands should hold the controller firmly, with thumbs positioned on the control sticks for precise and controlled movements. Avoid jerky or uncontrolled movements. The body should remain relaxed, allowing for smooth and coordinated actions.
Advanced Drone Techniques and Features
Advanced drone techniques and features enhance capabilities beyond basic flight. This section explores waypoint navigation, aerial photography, and advanced maneuvering.
Waypoint Navigation and Return-to-Home (RTH)
Waypoint navigation allows pre-programming a flight path, while RTH automatically returns the drone to its starting point. These features are particularly useful for complex shots or when losing visual contact.
Aerial Photography and Videography
Drones offer unique perspectives for photography and videography. Understanding camera settings, angles, and composition is crucial for capturing high-quality footage.
Camera Settings and Angles

Different camera settings and angles can significantly impact the final product. Experiment with various settings and angles to achieve the desired aesthetic and quality. Factors to consider include aperture, shutter speed, ISO, and focal length.
Advanced Maneuvering Techniques
Precise hovering and smooth transitions require practice and skill. Mastering these techniques allows for professional-looking shots and stable footage.
Drone Software for Flight Planning and Data Analysis
Specialized software facilitates flight planning, route optimization, and post-flight data analysis. These tools enhance efficiency and precision in drone operation.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Problems
This section addresses common drone malfunctions and provides solutions for troubleshooting various issues.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
Common problems include low battery, GPS signal loss, motor failures, and communication issues. Understanding potential causes helps in efficient troubleshooting.
Troubleshooting Solutions
Solutions vary depending on the specific problem. Low battery requires charging, GPS signal loss may require relocation, motor failures necessitate repair or replacement, and communication issues could stem from interference or controller problems.
Basic Drone Maintenance
Regular maintenance extends the drone’s lifespan. This includes cleaning propellers and the drone body, checking for loose parts, and lubricating moving parts as needed.
Extending Drone Battery Lifespan
Proper storage and charging practices extend battery lifespan. Avoid extreme temperatures and fully charge the battery only when needed.
Troubleshooting Guide
- Low Battery: Charge the battery fully.
- GPS Signal Loss: Move to an area with better GPS reception.
- Motor Failure: Inspect and replace faulty motors.
- Communication Issues: Check for interference and controller connection.
Legal and Ethical Considerations

Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding legal and ethical implications. This section Artikels relevant regulations and ethical considerations.
Drone Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Regulations vary by location and may restrict flight in certain areas, such as airports and restricted airspace. Always check local regulations before flying.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations include respecting privacy, avoiding intrusive surveillance, and ensuring public safety. Responsible operation requires awareness of potential impacts on others.
Restricted or Prohibited Drone Use
Drone use may be restricted or prohibited near critical infrastructure, during emergencies, or in areas with specific regulations.
Responsible Drone Usage
Responsible drone use involves adhering to regulations, respecting privacy, and ensuring safety. Always prioritize responsible and ethical operation.
Resources for Permits and Licenses
Depending on the intended use and location, permits or licenses might be required. Check local aviation authorities for information on obtaining necessary documentation.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of technical understanding, practical skills, and a strong commitment to safety and ethical conduct. By following the guidelines and best practices Artikeld in this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to confidently and responsibly explore the vast potential of drone technology. Remember, continuous learning and practice are key to honing your skills and expanding your capabilities as a drone pilot.
Safe flying!
Clarifying Questions
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and automated features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with good stability and intuitive controls.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model and flight conditions. Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes per charge, but always check your specific drone’s specifications.
What happens if I lose GPS signal?
Most drones have a “return-to-home” (RTH) function, which will automatically guide the drone back to its starting point. However, it’s crucial to practice flying in areas with good GPS reception.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific rules and regulations.
