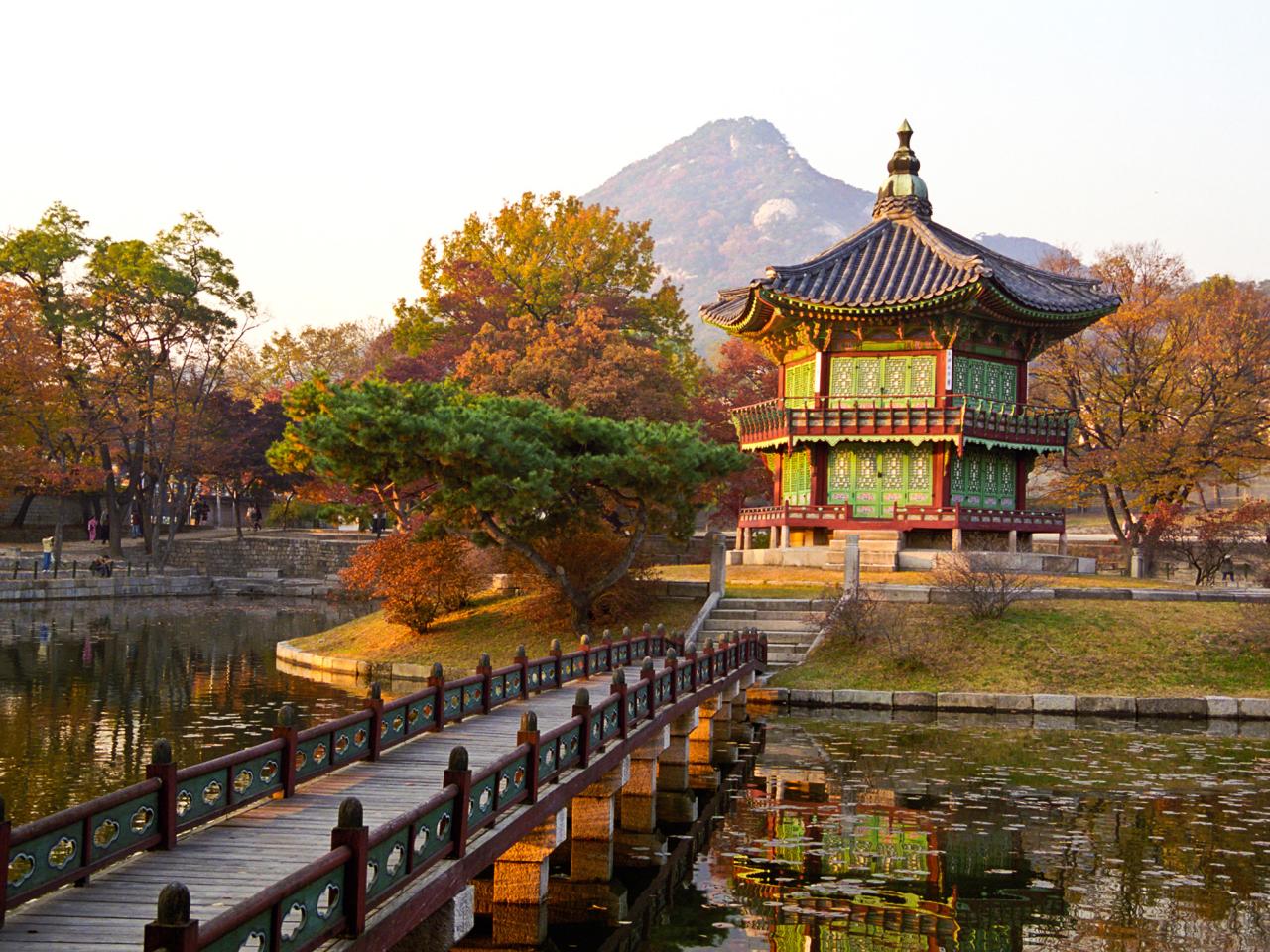
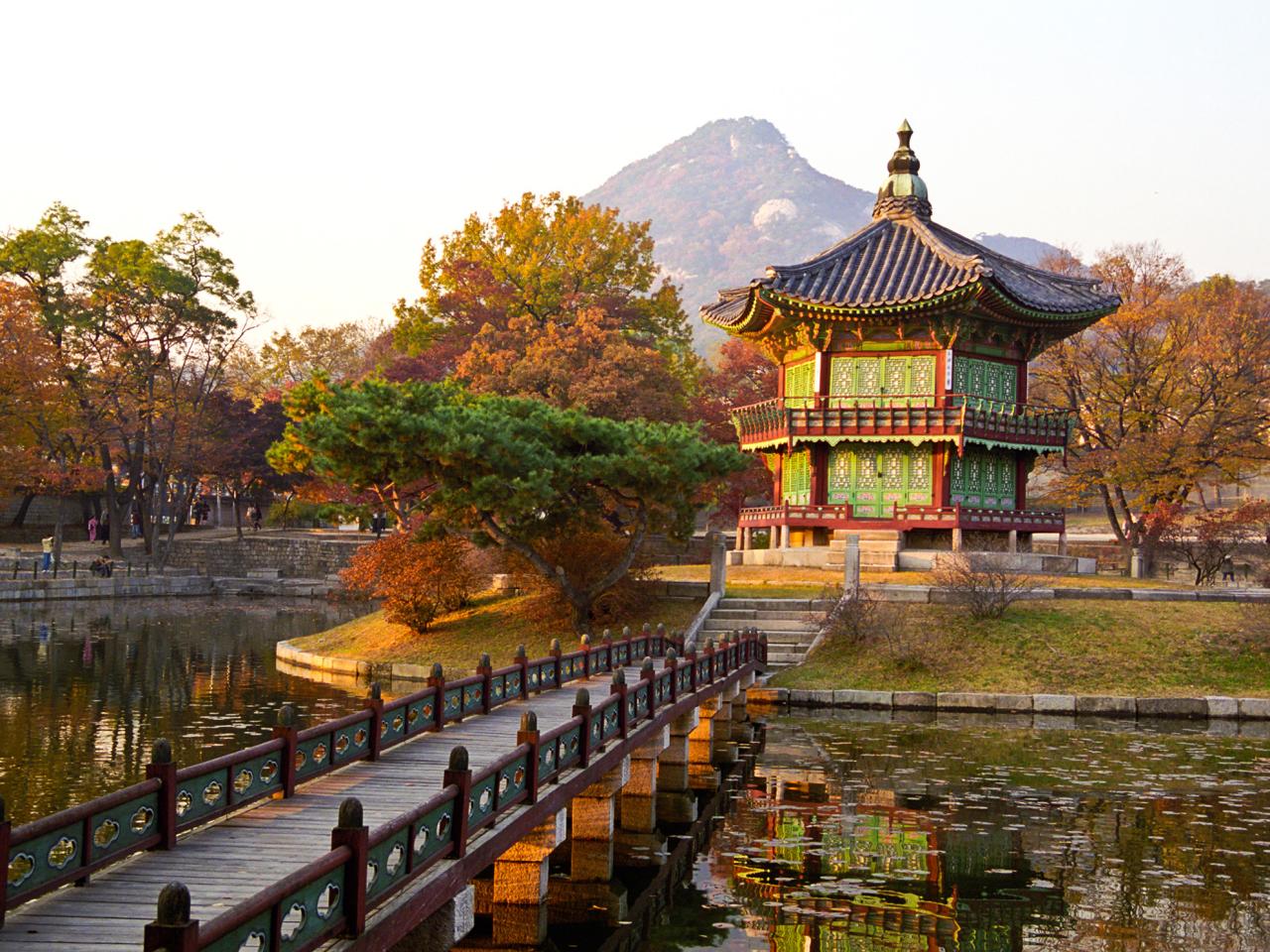
South Korea, a vibrant nation on the Korean Peninsula, boasts a fascinating blend of ancient traditions and cutting-edge technology. From its remarkable economic ascent to the global phenomenon of K-pop, South Korea’s story is one of resilience, innovation, and cultural dynamism. This exploration delves into the multifaceted aspects of this dynamic country, examining its economic powerhouse status, rich cultural heritage, complex political landscape, and significant geopolitical role.
South Korea’s global pop culture influence is undeniable, and a huge part of that is its captivating television. One show that really put South Korea on the map internationally was the wildly popular Squid Game, and now everyone’s buzzing about what’s next with the upcoming 5 squid game season 2. We can’t wait to see what new twists and turns the creators come up with, further showcasing South Korea’s creative prowess.
We’ll uncover the secrets behind South Korea’s economic success, exploring its key industries and comparing its economic model to that of its regional neighbor, Japan. We’ll also journey through its captivating culture, from the influence of Confucianism to the global impact of K-pop. Further, we will analyze its political system, its complex relationship with North Korea, and the technological innovations that have propelled it to the forefront of the global stage.
Finally, we’ll examine its social fabric, its unique cuisine, and the challenges it faces in the 21st century.
South Korea’s Economy
South Korea’s remarkable economic journey, from post-war devastation to becoming a global economic powerhouse, is a testament to its strategic planning and adaptability. This section delves into the key drivers of its growth, comparing its model with Japan’s, and exploring the challenges faced by its businesses in the global arena.
Key Sectors Driving South Korea’s Economic Growth
South Korea’s economic success is largely attributed to its focus on specific sectors. Electronics and automobiles are prominent, with companies like Samsung and Hyundai playing pivotal roles in global markets. Shipbuilding, steel production, and petrochemicals also contribute significantly to the nation’s GDP. Furthermore, the country has invested heavily in advanced technologies, including semiconductors and telecommunications, positioning itself at the forefront of technological innovation.
Comparison of South Korea’s and Japan’s Economic Models
Both South Korea and Japan followed export-oriented growth strategies, but their approaches differed. Japan focused on gradual, organic growth with a strong emphasis on domestic industries before expanding globally. South Korea, on the other hand, adopted a more rapid, aggressive approach, prioritizing export-led growth and leveraging foreign investment more extensively. This resulted in faster initial growth for South Korea but also exposed it to greater global economic volatility.
Challenges Faced by South Korean Businesses in the Global Market
Despite its success, South Korean businesses face significant challenges. Increasing competition from China and other emerging economies is a major concern. Furthermore, global trade disputes and fluctuations in exchange rates pose considerable risks. Maintaining technological leadership and adapting to changing consumer demands are also crucial for sustained growth.
Historical Economic Development of South Korea
| Period | Major Events | Economic Impact | Further Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Post-Korean War (1950s-1960s) | Reconstruction efforts, land reform, focus on light industry | Initial recovery and laying the foundation for future growth | Significant aid from the US played a crucial role. |
| Export-Oriented Growth (1970s-1980s) | Investment in heavy industries (steel, shipbuilding), Chaebol expansion | Rapid industrialization and economic expansion | The Chaebol, large family-controlled conglomerates, became major drivers of growth. |
| Technological Advancement (1990s-2000s) | Focus on electronics, telecommunications, and information technology | Transformation into a high-tech economy | Samsung and LG became global leaders in electronics. |
| Global Integration (2010s-Present) | Increased participation in global value chains, focus on innovation and sustainability | Continued economic growth, but facing new challenges from global competition | Efforts to diversify the economy beyond traditional sectors are underway. |
South Korean Culture
South Korean culture is a fascinating blend of tradition and modernity, deeply influenced by Confucianism and shaped by its unique history. This section explores the impact of Confucianism, showcases traditional art forms, examines the global phenomenon of K-pop, and highlights the key cultural differences between North and South Korea.
Influence of Confucianism on South Korean Society
Confucianism has profoundly shaped South Korean values and social structures. Emphasis on filial piety, respect for elders, and social harmony permeates family life and societal interactions. The emphasis on education and meritocracy is also a direct result of Confucian ideals, driving the nation’s commitment to academic excellence.
Traditional Korean Art Forms
Korea boasts a rich artistic heritage. Traditional painting, often featuring landscapes and calligraphy, reflects the nation’s aesthetic sensibilities. Pottery, particularly celadon ware, is renowned for its elegance and craftsmanship. Traditional music, with its distinctive instruments and melodies, adds another layer to the cultural tapestry.
Evolution and Global Impact of K-pop
K-pop’s rise as a global phenomenon is a testament to South Korea’s cultural influence. Its catchy melodies, sophisticated choreography, and visually stunning music videos have captivated audiences worldwide. K-pop’s global reach has not only boosted the South Korean economy but also significantly increased awareness of South Korean culture on a global scale.
Key Differences Between Northern and Southern Korean Cultural Practices
Decades of separation have led to significant cultural divergence between North and South Korea. While both share some historical roots, the distinct political ideologies and socio-economic systems have shaped vastly different cultural landscapes.
- Political Ideology and Propaganda: North Korea’s culture is heavily influenced by state-controlled propaganda, emphasizing loyalty to the regime and self-reliance, whereas South Korea’s culture is more diverse and open.
- Access to Information and Global Culture: South Koreans have greater access to global media and trends, leading to a more cosmopolitan outlook than their northern counterparts.
- Economic Development and Lifestyle: South Korea’s economic prosperity has resulted in a consumer-driven culture, a stark contrast to North Korea’s austere lifestyle.
- Artistic Expression: South Korea enjoys a vibrant and diverse arts scene, while artistic expression in North Korea is largely controlled and limited.
South Korea’s Political System
South Korea operates as a democratic republic, with a complex political system influenced by its unique history and societal values. This section details the structure of the government, the role of the president, and compares it to other democratic systems in Asia.
Structure and Functions of the South Korean Government
South Korea’s government is comprised of three branches: the executive (led by the president), the legislative (the National Assembly), and the judicial (the Supreme Court). The National Assembly is bicameral, consisting of the National Assembly and the Supreme Court. A system of checks and balances is in place to prevent any one branch from becoming too powerful.
Role of the President in South Korean Politics
The president serves as the head of state and government, wielding considerable power. The president appoints the prime minister and cabinet, sets the national agenda, and commands the military. Presidential elections are held every five years.
Comparison of South Korea’s Political System with Other Democratic Systems in Asia
Compared to other Asian democracies like Japan and India, South Korea’s political system exhibits both similarities and differences. While all three are democratic republics with elected legislatures, South Korea’s presidential system differs from Japan’s parliamentary system. The relative power of the executive branch also varies across these nations, reflecting their distinct historical and political contexts.
Process of Lawmaking in South Korea
The process of lawmaking in South Korea begins with the proposal of a bill, typically by a member of the National Assembly. The bill is then debated and voted upon in both houses of the assembly. If passed by both houses, it is sent to the president for approval or veto. The president’s veto can be overridden by a two-thirds vote in the National Assembly.
South Korea’s Geopolitical Position
South Korea’s geopolitical situation is complex and challenging, shaped by its proximity to North Korea, its strong alliances with the United States and other nations, and the lasting impact of the Korean War. This section explores these aspects, examining the challenges, relationships, and historical context.
Major Geopolitical Challenges Faced by South Korea
The most significant geopolitical challenge is the ongoing threat from North Korea, including its nuclear weapons program and potential for military conflict. Maintaining regional stability and managing the complex relationship with its northern neighbor requires delicate diplomacy and strategic alliances.
South Korea’s Relationship with North Korea
The relationship between South and North Korea is characterized by a mixture of tension and cooperation. While periods of dialogue and reconciliation have occurred, the underlying political and ideological differences remain a major obstacle to lasting peace.
South Korea’s Alliances and Partnerships with Other Countries
South Korea maintains strong alliances with the United States, Japan, and other countries in the region. These partnerships are crucial for security, economic cooperation, and maintaining regional stability. South Korea also actively participates in various international organizations and initiatives.
Impact of the Korean War on South Korea’s Geopolitical Landscape
| Date | Event | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| June 25, 1950 | North Korean invasion of South Korea | Initiation of the Korean War, leading to widespread devastation and division of the Korean peninsula. |
| July 27, 1953 | Korean War Armistice Agreement | Establishment of the Demilitarized Zone (DMZ), solidifying the division of Korea and creating a lasting source of geopolitical tension. |
| Post-War Period | US military presence in South Korea, economic aid, and development of a strong alliance | Significant influence on South Korea’s political, economic, and security policies. |
South Korea’s Technology and Innovation
South Korea’s remarkable technological advancements are a key driver of its economic success and global influence. This section highlights its progress in various sectors, showcases innovative companies, and examines the government’s role in fostering innovation.
Advancements in Electronics and Telecommunications
South Korea is a global leader in electronics and telecommunications. Companies like Samsung and LG are major players in the global market, producing a wide range of electronic devices and telecommunications equipment. The country’s robust infrastructure and investment in research and development have fueled these advancements.
Innovative South Korean Companies and Their Contributions

Beyond Samsung and LG, many other innovative South Korean companies contribute to the nation’s technological prowess. These include companies specializing in semiconductors, biotechnology, and other advanced technologies. Their contributions extend beyond the domestic market, shaping global technological trends.
Comparison of South Korea’s Technological Capabilities with Other Leading Nations

South Korea’s technological capabilities rival those of other leading nations such as the United States, Japan, and China. While the US and Japan may maintain a lead in certain specific areas, South Korea consistently ranks among the top nations in terms of technological innovation and competitiveness.
South Korea’s tech scene is booming, and you’ll see amazing drone photography showcasing its beautiful landscapes. If you’re looking for a powerful and reliable drone to capture those stunning views, check out the ae86 pro max drone ; its features are perfect for professional-level aerial shots. Then, after capturing those breathtaking images, you can share your South Korean adventure with the world!
Government’s Role in Fostering Technological Innovation
The South Korean government plays a crucial role in fostering technological innovation through strategic investments in research and development, support for technology startups, and the creation of favorable regulatory environments. This proactive approach has been instrumental in driving the nation’s technological advancements.
- Investment in R&D: Significant government funding is allocated to research and development across various technological sectors.
- Support for Startups: Numerous programs and initiatives are designed to support and nurture technology startups.
- Regulatory Environment: The government strives to create a regulatory framework that encourages innovation while maintaining appropriate standards.
- Collaboration: Strong emphasis is placed on collaboration between government, industry, and academia.
South Korean Society and Social Issues
South Korean society, while highly developed, faces a range of social challenges common to many advanced economies. This section explores prevalent issues such as income inequality and an aging population, examines the role of education, and compares its social welfare system with others.
Social Issues in South Korean Society
South Korea grapples with issues such as income inequality, widening the gap between the rich and the poor. The rapidly aging population presents challenges for the social security system and healthcare infrastructure. High levels of stress and competition, particularly in education and employment, also contribute to social anxieties.
Role of Education in South Korean Society
Education plays a central role in South Korean society, viewed as a key to social mobility and economic success. The emphasis on academic achievement is intense, leading to highly competitive educational systems. This intense focus, however, has also resulted in concerns about student well-being and mental health.
Comparison of South Korea’s Social Welfare System with Other Developed Nations
South Korea’s social welfare system is constantly evolving, striving to meet the changing needs of its population. Compared to other developed nations, its social safety net may be less extensive in certain areas, but it continues to expand to address challenges such as aging and healthcare costs.
Common Social Values in South Korea
| Family | Work | Community | Individual |
|---|---|---|---|
| Filial piety, family unity, respect for elders | Hard work, dedication, perseverance, collectivism | Social harmony, cooperation, community involvement | Self-improvement, education, achievement |
South Korean Food and Cuisine
South Korean cuisine is renowned for its diverse flavors, vibrant colors, and unique culinary traditions. This section explores the characteristics of traditional Korean food, provides examples of popular dishes, and discusses its cultural significance.
Characteristics of Traditional Korean Cuisine

Traditional Korean cuisine emphasizes balance and harmony of flavors, often incorporating a variety of ingredients like rice, kimchi, meat, vegetables, and seafood. The use of fermented foods like kimchi is a hallmark of Korean cooking, adding a distinctive tangy and spicy element to many dishes.
Popular Korean Dishes and Their Ingredients, South korea
Bibimbap, a mixed rice dish with assorted vegetables and meat, is a classic example of Korean cuisine. Bulgogi, marinated grilled beef, is another popular dish, often served with various side dishes called banchan. Kimchi jjigae, a spicy kimchi stew, is a flavorful and comforting option.
Cultural Significance of Food in South Korean Society
Food plays a significant role in South Korean society, often used to express hospitality, celebrate occasions, and strengthen social bonds. Sharing meals is a common way to foster relationships and build community. Food also holds symbolic meaning, often reflecting seasonal changes and cultural traditions.
A Traditional Korean Meal
Imagine a traditional Korean meal, meticulously arranged on a low table. A steaming bowl of bibimbap sits in the center, surrounded by an array of vibrant banchan – kimchi, seasoned spinach, pickled radish, and other colorful accompaniments. The aroma of the gently sizzling bulgogi fills the air, mingling with the tangy scent of kimchi. The meal is a feast for the senses, a reflection of Korean culinary artistry and cultural values.
South Korea, a land of vibrant culture and delicious food, has captivated the world with its unique storytelling. A huge part of this global fascination comes from the hit Netflix show, Squid Game, and everyone’s asking, “Check out this link to find out when is season 3 of squid game ,” so we can all get back to enjoying more amazing Korean entertainment.
Hopefully, the wait won’t be too long before we’re once again immersed in the gripping world of South Korean drama.
The atmosphere is one of warmth and conviviality, with family and friends gathered together to share the meal and enjoy each other’s company. It’s a moment of connection, a celebration of both food and fellowship.
Epilogue
South Korea’s journey is a testament to the power of adaptation, innovation, and a strong national identity. From its post-war reconstruction to its current position as a global leader in technology and culture, the nation’s story is one of remarkable achievement and ongoing evolution. Understanding South Korea’s complexities provides valuable insights into the dynamics of East Asia and the challenges and opportunities facing nations in a rapidly changing world.
Its blend of tradition and modernity offers a compelling case study for economic development, cultural influence, and geopolitical strategy.
Key Questions Answered
What is the official language of South Korea?
Korean.
What is the currency of South Korea?
South Korean Won (KRW).
What is the capital city of South Korea?
Seoul.
What is the population of South Korea?
Approximately 51.8 million (this number fluctuates, check for the most up-to-date data).
What is South Korea’s most popular sport?
Baseball and football (soccer) are both extremely popular.
